Cyber security, Unveiling the Cyber Threat Landscape: Safeguarding Your Digital Assets in an Evolving World
Insights from a Recent Talk with LTIMind Tree: Path to Effective Cybersecurity
Intro
Greetings, readers! Today, we are gonna deep dive into the world of Cyber security and cyber threats. This article represents Insights from a recent talk with LTIMind Tree by Chakravarthy (Chakry) YSSKK - Director: Program & Project Management at LTIMindtree ( LinkedIn ) conducted by Vardhaman College of Engineering. In collaboration with Vardhaman College of Engineering, I had this opportunity to engage in a stimulating discussion with Mr Chakry from LTIMindtree, a prominent global IT services and solutions company. During this insightful interaction, I explored various aspects of cybersecurity and gained valuable insights into their expertise in the field and here goes what I learned.
About LTIMindtree
LTIMindtree is a global technology consulting and digital solutions company that enables enterprises across industries to reimagine business models, accelerate innovation, and maximize growth by harnessing digital technologies. As a digital transformation partner to more than 700+ clients, LTIMindtree brings extensive domain and technology expertise to help drive superior competitive differentiation, customer experiences, and business outcomes in a converging world. Powered by nearly 90,000 talented and entrepreneurial professionals across 30+ countries, LTIMindtree — a Larsen & Toubro Group company — combines the industry-acclaimed strengths of erstwhile Larsen and Toubro Infotech and Mindtree in solving the most complex business challenges and delivering transformation at scale. For more info, please visit www.ltimindtree.com ( From about LinkedIn LTIMindtree)

Impact of Cyber security :
Asking ransom
--> Demanding payment from a victim or organization in exchange for resolving a cyber attack or releasing encrypted data.
Industrial espionage
--> Gathering of confidential or valuable information from companies without their permission
Selling to criminals
--> Selling to criminals means knowingly providing goods or services to individuals involved in illegal activities.
Using for crime
--> Act of utilizing something, such as tools, or technology, with the intent to commit illegal activities or offences.
Examples of cyber attacks :
DDoS( Distributed Denial-of-Service )
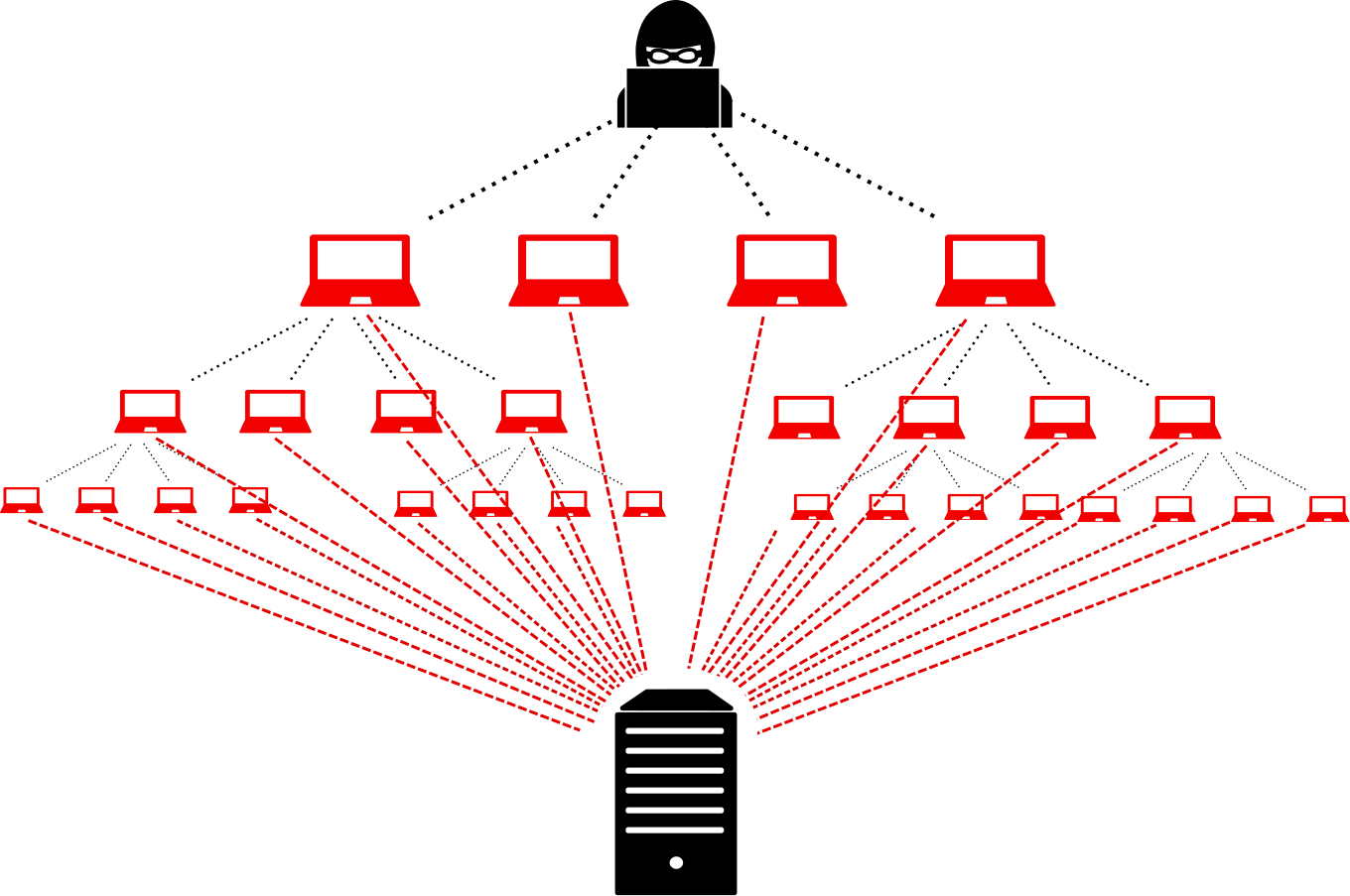
--> The goal of a DDoS attack is to make a website or online service unavailable to its intended users, causing inconvenience, financial losses, and reputational damage to the targeted entity.
example by Mr Chakry: Blocking booking of tickets in cricket stadium to make stadium owners fall in the loss.
Malware ( short for malicious software )
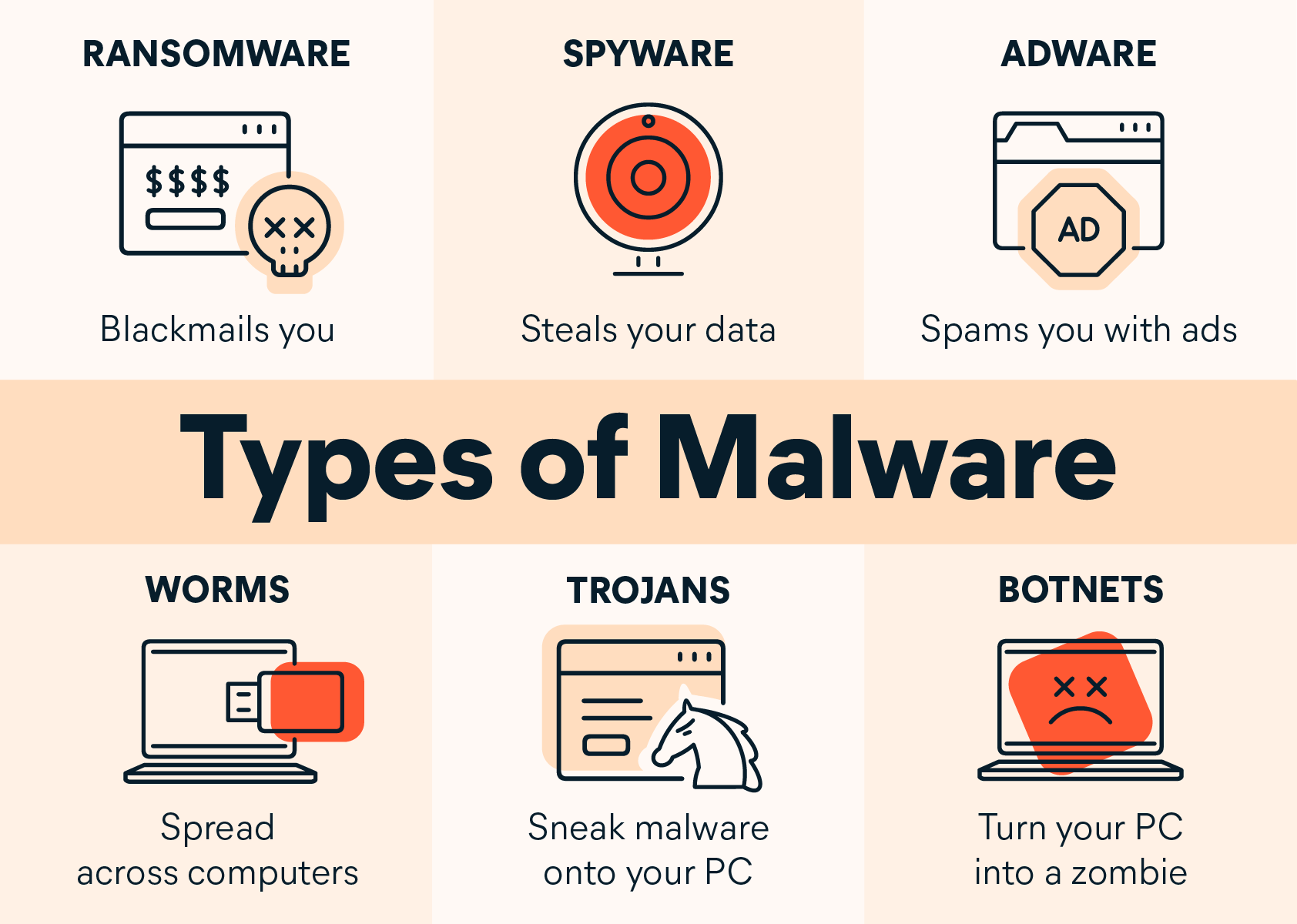
--> refers to any software specifically designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems, networks, or user devices.
some types are Viruses, Worms, Trojans, Ransomware, Spyware, Adware
, Keyloggers.
Phishing

Phishing is a type of cyber attack where attackers attempt to deceive individuals into providing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, credit card details, or personal data, by anonymous links.
Credential attack
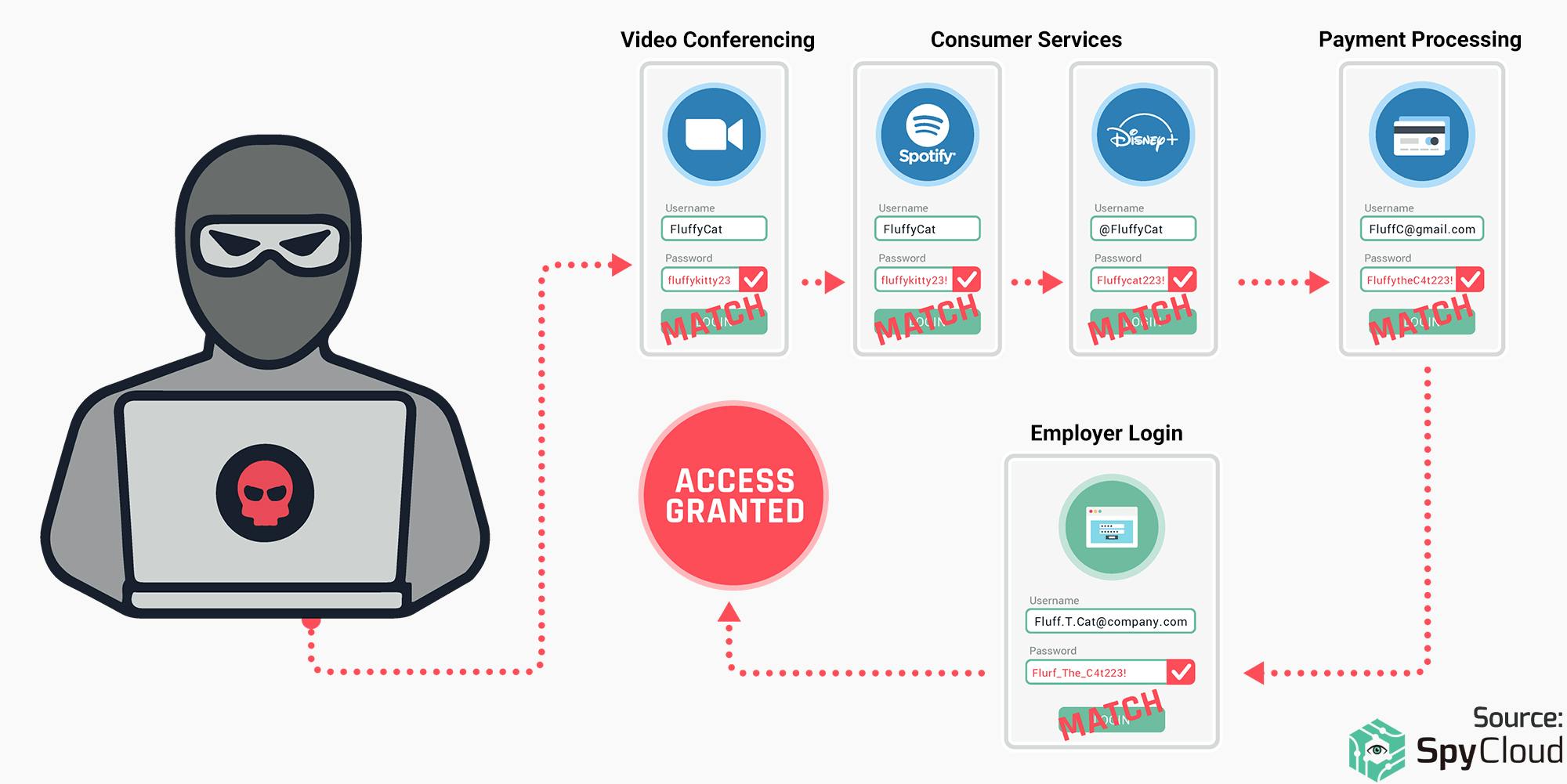
It is a type of cyber attack where an attacker aims to steal user credentials, such as usernames and passwords, to gain unauthorized access to accounts, systems, or networks.
The motive of cyber attacks
Disrupting business continuity
Info theft and manipulation of data
Creating fear and chaos by disrupting physical infrastructure
Financial loss to the target
Acheivig state military objective
demanding ransom
damaging reputation
Types of attackers
Black Hat Hackers( malicious hackers / illegal hackers )

Black hat hackers, also known as malicious hackers or crackers, are individuals who engage in hacking activities for personal gain, or to cause harm.
The opposite of white hat hackers, black hat hackers have only one intention – to create chaos and get away with the spoils. They target systems of government and big businesses with the wrong intentions of stealing information from them.
key characteristics :
Unauthorized Access
Malicious Activities
Exploiting Vulnerabilities
Red Hat Hackers( Opposes black hat illegally )

Red hat hackers, also known as ethical hackers or vigilante hackers, are individuals who use their hacking skills and knowledge for the greater good or to expose vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, or software.
In simple words, they stop the black hat hackers from stealing information in the black hat hackers way that is illegally
Red hats are the frontline warriors against black hats. A red hat hacker directly targets and fends off the attacks of different types of hackers’ hats. They are known to be pretty ruthless when dealing with black hats.
Green Hat Hackers(Newbie hacker)

This represents a beginner or novice hacker who is enthusiastic about learning and exploring the field of cybersecurity. These individuals may have limited knowledge or experience but possess a strong interest in hacking and aim to develop their skills.
Green hat hackers are newbies to the hacking world. They are still learning and have not mastered the science of hacking yet. They typically hack low-end systems of other individuals and are not interested in hacking bigger yet.
They usually follow other types of hackers, intending to learn from them.
Grey Hat Hackers( Newbie hacker )

Grey hat hackers are the nerdiest and geekiest hackers among all other types of hackers. They do not fall under black or white hackers because they hack not for any particular motive. These hackers hack only for the fun of it.
Blue Hat Hackers(learning hacking )

Like green hat hackers, blue hat hackers are other types of hackers that are also new to hacking. Their aim is also to learn how to hack, mainly focusing on what they do not know yet.
for taking revenge they learn hacking
White Hat hackers

White hat hackers are some of the best hackers in the world. They specialize in all matters related to cybersecurity and can hack them to destroy systems or strengthen them.
The security goal of a Company (Should be followed by every employee)
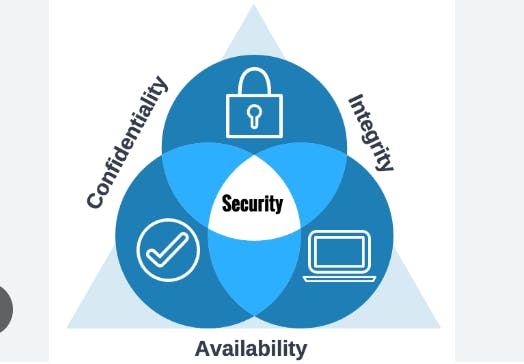
Confidentiality
Ensure private or confidential information is not being disclosed to unauthorized individuals.
Integrity
Ensure data & systems are free from unauthorized manipulation.
Availability
Ensure systems work promptly for their intended use and service is not denied to authorized users.
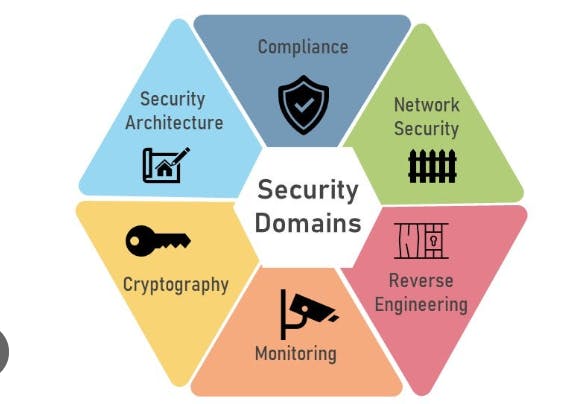
Security Domains
Do's in cyber security
Use strong and unique passwords.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA).
Keep software updated.
Use reliable security software.
Practice safe browsing.
Regularly back up your data.
Educate yourself and your employees.
Secure your Wi-Fi network.
Implement firewall protection.
Create regular data backup and recovery plans.
Do not's in Cyber security
Don't reuse passwords across multiple accounts.
Don't click on suspicious links or download files from unknown sources.
Don't share sensitive information through unsecured channels.
Don't disable or ignore security updates.
Don't leave devices unattended or unlocked.
Don't overshare personal information on social media.
Don't use public Wi-Fi networks without proper security precautions.
Don't open email attachments from unknown or suspicious senders.
Don't fall for phishing scams or provide personal information in response to unsolicited requests.
Don't neglect to regularly review and monitor your financial accounts for any unauthorized activity.
Certifications
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
CompTIA Security+
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)

